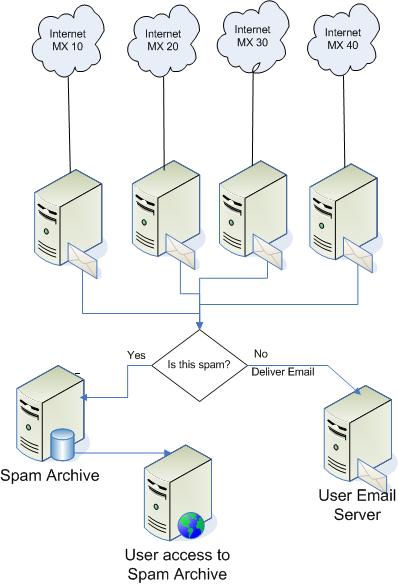
This is how NITF E-mail Filtering Services works:
Which Emails Can Be Blocked
(Blacklisted)
- Images -
NITF is able to scan inside images embedded
in emails for spam content.
- DNS RBL
Servers - Our NITF
servers checks the IP address initiating the
connection. If it is listed in one of its many DNS
RBL blacklist servers the connection is refused.
- SURBL
Servers - NITF scans the content of emails
for any HTTP links and URLs. Every link found is
then tested against one of the many SURBL DNS
blacklists available. If present, the connection is
refused.
- IP Blacklist -
Our
NITF servers checks if the
remote server's IP address matches an entry in our
IP blacklist file, the email is rejected.
- Domain Blacklist -
The NITF gateway checks if the
domain portion in the sender's email address is in
our domain blacklist file, the email is also
rejected.
- Country Blacklist -
The sender's Country is tested
to see if it is in your list of undesired countries.
If so, the email is refused. This product includes
GeoIP data created by MaxMind, available from
http://maxmind.com.
- FROM EMail Blacklist -
The sender's email
address is checked against our list of blacklisted
email addresses. If present, it is rejected.
- TO EMail Blacklist -
The recipient's email address is
checked against our list of blacklisted email
addresses. If present, it is rejected.
-
Attachment Blocking -
NITF can check emails for specific attachments or
attachment extensions. If found, the email is
rejected.
- Keyword Content Filtering -
NITF can check email
content and subject for specific keyword and/or
phrases. If found, the email is rejected.
-
Bayesian statistical DNA fingerprinting -
NITF features statistical DNA fingerprinting of
incoming emails. This filter is self-learning,
continuously analyzing your incoming traffic to
improve its accuracy with time.
- SPF - Sender Policy
Framework - SPF fights email address forgery
and makes it easier to identify spam, worms, and
viruses. Domain owners identify sending mail servers
in DNS. NITF verifies the envelope sender address
against this information, and can distinguish
legitimate mail from spam before any message data is
transmitted.
- Honeypot Emails - We
have a list of "honeypot" email addresses. Any email
sent to an address in the list will cause the
sender's IP to be blacklisted.
- Additional anti-spam tests
- NITF can then
optionally check to see if the recipient address has
a % sign in it. Many SMTP servers are susceptible to
being tricked into relaying with this. Connections
can be rejected if the remote server does not have a
reverse DNS PTR entry. NITF is able to check if the
sender's MX DNS record is valid before accepting
email. You can also refuse connections if the remote
server attempts more than n RCPT TOs in a single
connection or if there are too many spaces in the
subject line.
Which Emails Are Allowed (Whitelisted)
- Allowed domains -
If the IP passes the DNS tests
NITF then checks the recipient domain. If your
domain is listed as an allowed domain, then the
recipient is accepted. This is done to prevent
spammers to use NITF to relay.
- Excluded IPs -
If an IP is blacklisted, but you
really need to be able to receive email from that
domain anyways, the domain can be added in an
exclude list as to allow it to bypass the blacklist
rules.
- Excluded Domains -
If an IP is blacklisted but you
still wish to receive email from them, the IP can be
added to an IP exclude list to allow it to bypass
the blacklist rules.
- Unfiltered Emails -
If you have users who do not
want to receive filtered emails, they can be
accommodated by adding them to a pass-list. EMails
addressed to them will bypass all of NITF rules.
- Excluded FROM Emails -
If you want a sender's
email address to be excluded from all filtering
rules, you can add it to an exclude list.
- Authorized TO EMails -
If you want NITF to only
deliver emails to specific addresses in your
domain(s), you can manage such a list.
- Keyword whitelisting -
You can provide your customers with specific
keywords that, if found in the body or subject of
emails, will bypass all filtering rules.
Other Features
- NITF will reject an email if
it considered as spam and archive those emails
rather than having them lost. The remote server will
still receive an error stating that the email was
rejected, but you will keep a copy in the quarantine
website. This will allow you to force delivery of
legitimate email which could have been filtered.
- Enable Cached
IP Blocking - If an IP address sends more
than a certain number of spam emails (10) during a
certain time interval (10 minutes), then it can be
temporarily banned (blacklisted). All further
connections from that IP address will be immediately
rejected without allowing the sender to transmit any
data. This greatly reduce the load on the server. A
banned IP address will be automatically removed from
this temporary blacklist after a defined time
interval (60 minutes).
- Reject if no reverse DNS -
NITF rejects emails if
the remote server does not have a valid reverse DNS
PTR entry.
- Reject if Empty "Mail From"
- NITF will reject all
emails with an empty "Mail From" field.
- Reject if "Mail From" =
"Mail To" - Reject all
emails where the sender's email is the same as the
recipient's email.
- Reject if "From Domain" =
"To Domain" - NITF
rejects all emails where the sender's domain is the
same as the recipient's domain. Your users will not
go through NITF when sending emails to themselves,
Spammers often use this technique.
Black/Whitelists Tab
- BLACKLISTS MAPS Blacklist
servers - NITF checks the
IP address initiating the connection. If it is
listed in one of its many DNS blacklists the
connection is refused. NITF can reject connections
based on a configurable minimum number of matches.
- Blacklisted IPs -
You can keep a file with
additional IPs that you want to blacklist by
entering the filename below. If the file does not
exist it will be created. The file is reloaded every
minute. List individual IP addresses on each line.
Use an ending .0 for a Class C wildcard (i.e.
192.12.45.0 to block 192.12.45.1 --> 192.12.45.255).
The contents of the file will be loaded in the memo
box, allowing you to make changes to the file.
- Blacklisted Domains -
You can keep a file with
additional Domains that you want to blacklist (based
on the MAIL FROM field) by entering them below
below. Enter one domain per line, no wildcards
allowed. If the file does not exist it will be
created. The file is reloaded every minute. The
contents of the file will be loaded in the memo box,
allowing you to make changes to the file.
- Blacklisted Emails -
If you want to block any
particular email addresses, enter them here, one
email per line.
- Country Filters -
NITF checks the what country
incoming connections are coming from. The current
number of connections for each country can be
updated by clicking on the Update Stats Now button.
Columns can be sorted by clicking on the column
header. This will help you in sorting countries and
hits so you can determine if there are any countries
you do not wish to receive email from.
- Attachment
Blocking - You can block emails that have
unwanted attachments. You can keep a file with
banned attachments here. check emails for specific
attachments or attachment extensions. If the
attachment is found, the email is rejected.
Whitelists
- Local Domains -
NITF will only deliver email to
the domains listed here. If the domain in the RCPT
TO email address is listed as a local domain, then
the recipient is accepted. This is done to prevent
spammers to use NITF to relay email to third party
email addresses/servers. If you need to have any
domain listed here forward its destination email to
a different server than the default destination
server, you can specify so here. You can override
the default destination server by appending the
forwarding mail server and port to any domain in
this list. The syntax should be as follows:
DomainName:DestinationServer:DestinationPort -
example: logsat.com:mail.netwide.net:25
- Excluded Domains / IPs -
Add here any "MAIL FROM"
domains or any IPs from which you want to receive
email if they would be blocked by any of your
blacklist rules. Enter as many IPs or domains as you
wish, one per line.
- Unfiltered Emails -
Any local email address listed
here will cause NITF to bypass all blacklist rules
for it. If you have any users who do not want to
have their email filtered, enter them here.
- Keywords Filter - You can
check email content and subject header for specific
keyword and/or phrases. If found, the email is
allowed through the filters. Useful if you want to
allow certain customers to send you email without
having to place them all in a email address
whitelist. The same syntax rules as the blacklist
keywords apply.
Customized Items
- Most rejection notices to
the remote servers can be customized. In the error
string you can embed the following
connection-specific parameters:
- %IP% -
The IP address of the remote
server connecting to NITF
- %Domain% -
The MAIL FROM domain name of the
incoming email attemp
- %EMailTo% -
The recipient of the incoming
email attempt
- %EMailFrom% -
The sender's email address
Bayesian Statistical Filtering
NITF features statistical DNA
fingerprinting of incoming emails. The statistical
analysis is performed using Bayesian rules. Tokens
within incoming emails are scanned and categorized in a
corpus file. The content of all new incoming email is
fingerprinted and checked against the historical data.
If there is a high statistical probability that the
email is spam, it is rejected. This is done to build a
valid statistical base to use before emails are
rejected. During this period of time, it is critical to
avoid false positives. If a good email is quarantined,
forcing it's redelivery thru the web interface will
"teach" NITF that the fingerprint in that email is a
"good" one, and the statistical DNA database will adapt
itself to it. It is very important initially to check
the quarantine often to force delivery of legitimate
email that has been blocked by the "regular" filtering
rules.
SPF - Sender Policy Framework
SPF is an open source standard that is
emerging as a solution to prevent spammers from using
fake email addresses. The following description was
taken from the official SPF website at
http://spf.pobox.com:
Domains use public records (DNS) to direct requests
for different services (web, email, etc.) to the
machines that perform those services. All domains
already publish email (MX) records to tell the world
what machines receive mail for the domain.
SPF works by domains publishing "reverse MX" records
to tell the world what machines send mail from the
domain. When receiving a message from a domain, the
recipient can check those records to make sure mail
is coming from where it should be coming from.
With SPF, those "reverse MX" records are easy to
publish: one line in DNS is all it takes. Suppose a
spammer forges a hotmail.com address and tries to
spam you.
He connects from somewhere other than hotmail.When
his message is sent, you see MAIL FROM: <forged_address@hotmail.com>,
but you don't have to take his word for it.
You can ask Hotmail if the IP address comes from
their network.
(In this example) Hotmail publishes an SPF record.
That record tells you (your computer) how to find
out if the sending machine is allowed to send mail
from Hotmail. If Hotmail says they recognize the
sending machine, it passes, and you can assume the
sender is who they say they are. If the message
fails SPF tests, it's a forgery. That's how you can
tell it's probably a spammer.
NITF looks up SPF DNS records for
all incoming emails. If an SPF record exists, the query
results can be any one of the following:
- Pass: the message meets the domain's definition
of legitimacy.
- Neutral : the message does not meet a domain's
definition of
legitimacy, but the SPF client MUST proceed as if a
domain did not
publish SPF data. Likely used by domains in
transition phase
who are beginning to adopt SPF.
- Softfail : the message does not meet a domain's
strict
definition of legitimacy, but the domain cannot
confidently state
that the message is a forgery.
- Fail : the message does not meet a domain's
definition of
legitimacy.
If the result is "Pass" the email
will pass the SPF filter.
This latest filter is proving to be one of the most
effective and accurate tools in stopping spam.
Anytime NITF ISP blocks an email, the
sender's IP address is sent to our centralized SFDB
database. This allows the SFDB filter to have access to
a huge repository of spammer's IPs, updated in real-time
by all the NITF ISP installations in the world. IP
addresses from the database are automatically aged and
removed from the database within 6-24 hours if they stop
sending spam and/or viruses.
The SFDB filter detects spam by
checking IP addresses against the SFDB database. The
"network reliability" level tells NITF how many
different users must have reported a specific IP in
order to classify it as spam.
Call us at 703-383-3900 with any question you may have between
9:00 am to 5:00 pm EST. |




